HAL & Hardware Drivers
Executive Summary
The power of AP_HAL_ChibiOS lies in its ability to abstract complex STM32 peripherals into standard interfaces. The most complex and critical part of this is the Shared DMA system, which allows ArduPilot to use more peripherals than there are DMA channels available.
Theory & Concepts
1. The ChibiOS HAL Driver Model
ChibiOS provides "High Level Drivers" (e.g., SerialDriver, SPIDriver) that abstract the register interface.
- Config: Drivers are configured with
Configstructs (baud rate, start bits) passed tosdStart(). - Events: Drivers trigger callbacks or wake threads on interrupts (TX Complete, RX Not Empty).
2. DMA Contention
STM32 chips have limited DMA Streams (e.g., 2 controllers x 8 streams = 16 streams).
- The Problem: We might have 10 UARTs, 3 SPIs, 2 I2Cs, and SD Card. That's > 16 potential users.
- The Solution:
Shared_DMA. A custom ArduPilot allocator that assigns a DMA channel to a driver only while a transaction is active and releases it immediately after.
3. Bounce Buffers
DMA engines access RAM directly. If that RAM is in a specific region (like CCM RAM on F4) or cached (D-Cache on F7/H7), DMA fails.
- Solution: We use "Bounce Buffers" in DMA-safe memory regions (SRAM1/2).
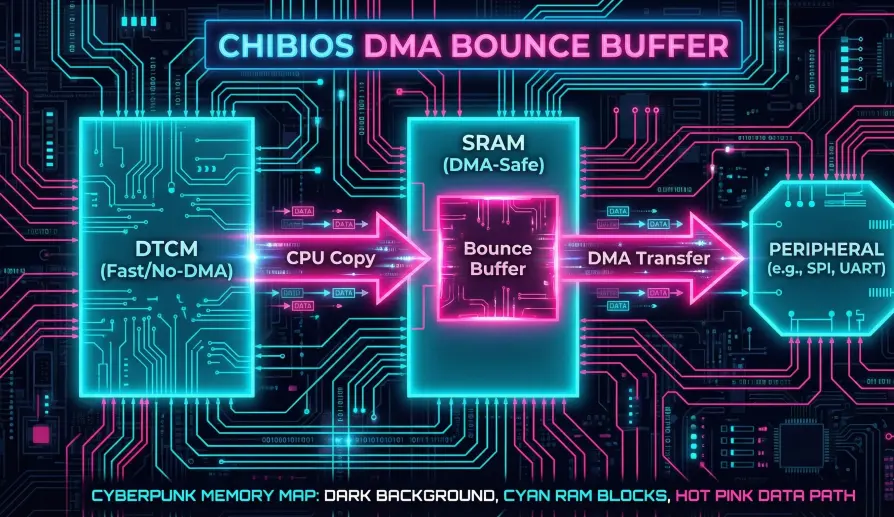
- Flow: User Buffer -> memcpy -> Bounce Buffer -> DMA -> Peripheral.
Codebase Investigation
1. UART Driver: UARTDriver.cpp
Located in libraries/AP_HAL_ChibiOS/UARTDriver.cpp.
- Initialization: Calls
sdStart(&SDx, &config). - RX: Uses a dedicated thread (
uart_rx_thread) or 1kHz timer (_rx_timer_tick) to move data from the ChibiOS ring buffer to the ArduPilot ring buffer. - DMA:
dmaStreamAllocIrequests a stream.
2. Shared DMA: shared_dma.cpp
This file implements a mutex-protected allocator.
- Locking: Before starting an SPI transaction, the bus driver calls
dma.lock(). - Contention: If the DMA stream is busy (used by another peripheral on the same stream ID), it blocks until available.
3. SPI Device: SPIDevice.cpp
Handles the complexity of the "Device" abstraction (Sensors on a Bus).
- Transactions:
get_semaphore()->take()ensures exclusive access to the bus (e.g., MPU6000 and Barometer on the same SPI bus). - CS Pin: Manually toggles the Chip Select pin via
palClearLine(dev->cs_pin).
Source Code Reference
Practical Guide: Porting Drivers
If you are adding a new sensor:
- Don't write raw registers.
- Use
AP_HAL::get_HAL().spi->device(...)to get a handle. - Respect the semaphore. Always wrap transfers in
bus->get_semaphore()->take().