Threading & Scheduling
Executive Summary
While the ArduPilot Flight Code (Copter/Plane) is largely single-threaded (the "Main Loop"), the underlying system is highly multi-threaded. AP_HAL_ChibiOS creates dedicated threads for I/O, storage, and RC handling to ensure that slow operations (like writing to an SD card) never block the flight stabilization loop.
Theory & Concepts
1. Static Thread Allocation
In embedded safety-critical systems, dynamic thread creation is risky (heap fragmentation). ChibiOS allows Static Allocation:
- Working Area: A statically defined array (e.g.,
static THD_WORKING_AREA(_io_thread_wa, 2048);) acts as the stack for the thread. - Benefits: We know exactly how much RAM is used at compile time.
2. Cooperative vs. Preemptive
- ArduPilot Main Loop: Runs in the
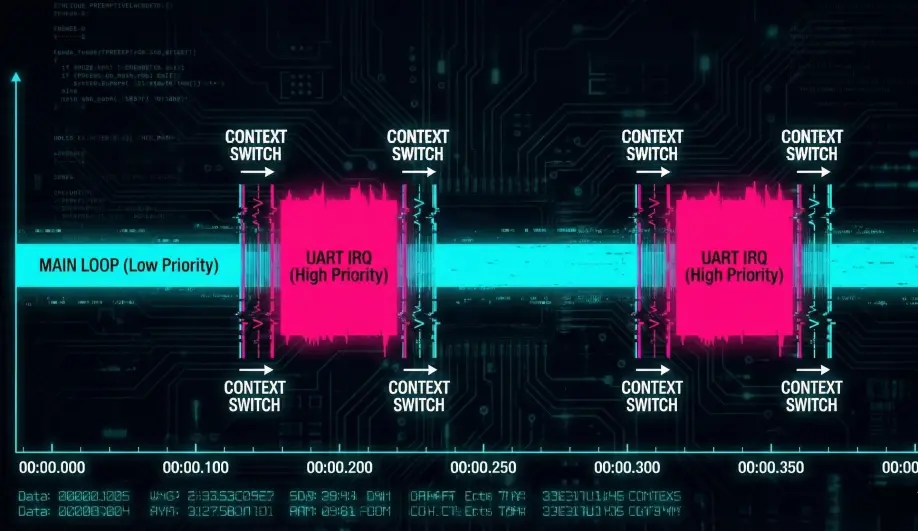
mainthread. It is cooperative internally (tasks must yield), but the thread itself is preemptable by the OS. - Driver Threads: Run asynchronously. For example, the UART driver receives bytes via DMA and signals a semaphore to wake up the I/O thread.
Codebase Investigation
1. Thread Creation: Scheduler::init()
Located in libraries/AP_HAL_ChibiOS/Scheduler.cpp.
ArduPilot spawns the following core threads:
_timer_thread: Runs 1kHz periodic tasks._rcin_thread: Decodes PPM/SBUS signals._io_thread: Low-priority background tasks (logging, files)._storage_thread: Handles EEPROM/FRAM emulation on flash._monitor_thread: Watchdog that checks for thread lockups.
2. The Yield: delay_microseconds()
When the main loop calls hal.scheduler->delay(1), it calls chThdSleep(ticks).
- This moves the Main Thread to the SLEEPING state.
- The ChibiOS scheduler immediately context-switches to the next highest priority READY thread (e.g., UART processing).
3. Priority Hierarchy
Priorities are defined in AP_HAL_ChibiOS.h (mapped to ChibiOS levels):
- SPI/I2C High Priority: Drivers that need instant bus access.
- Main Thread (Flight Loop): Above normal I/O.
- Timer Thread: 1kHz ticks.
- RC Input: Needs low latency capture.
- IO / Storage: Lowest priority. Can take milliseconds to run without affecting flight.
Source Code Reference
- Thread Spawning:
libraries/AP_HAL_ChibiOS/Scheduler.cpp - Stack Definitions: Look for
THD_WORKING_AREAmacros.
Practical Guide: Analyzing Stack Usage
Running out of stack causes a HardFault.
- Check: Set
HAL_CHIBIOS_ENABLE_STACK_CHECKto 1 inhwdef.dat(dev boards only). - Monitor:
Scheduler::check_stack_free()fills the stack with a pattern (0x55) and counts unused bytes. - Output: 'Stack Low' messages in the console/logs if a thread gets dangerously close to its limit.