Terrain Estimation (EKF)
Executive Summary
For precision landing and optical flow, the drone must know its height above the ground (AGL), not just its height above sea level (ASL). The EKF maintains a dedicated Terrain State that tracks the ground level relative to the Home Altitude. This allows the EKF to seamlessly fuse Rangefinder data with Barometer data.
Theory & Concepts
1. Laser Time-of-Flight (Lidar)
Most modern rangefinders use Lidar.
- The Physics: The sensor sends a pulse of light and measures the time it takes to return. Since light travels at a constant speed, the distance is calculated with millimeter precision.
- The Difference: Unlike a Barometer (which measures air pressure weight), Lidar measures physical distance.
- Terrain Persistence: ArduPilot doesn't just use the current Lidar reading; it maintains a "Terrain State." This means if you fly over a hole, the EKF knows the ground just "dropped" but the drone's altitude (relative to takeoff) is still the same.
2. Above Ground Level (AGL) vs. Mean Sea Level (MSL)
- MSL: Your height relative to the ocean (used by planes).
- AGL: Your height relative to the dirt below you (used by drones for landing).
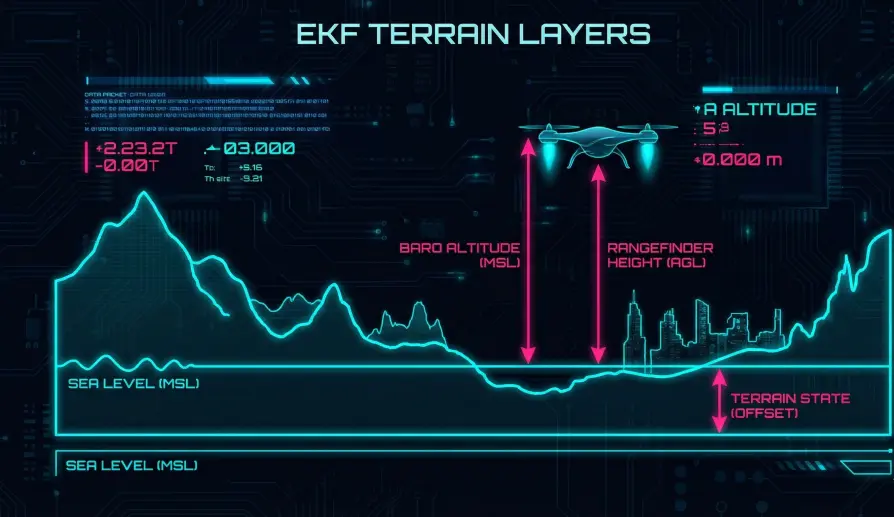
- The EKF Role: The EKF tracks MSL as its primary state and AGL as a "Terrain Offset" state. This allows it to fly a mission at a fixed MSL while simultaneously knowing its AGL for safety.
Architecture (The Engineer's View)
1. The Terrain State (terrainState)
The EKF tracks a single variable: Terrain Vertical Position (in NED frame).
- Definition: If the drone is at 10m Altitude (Baro) and the Rangefinder says "2m", the Terrain State is 8m.
- Code Path:
NavEKF3_core::EstimateTerrainOffset().
2. Rangefinder Fusion
When a Rangefinder is active:
- Prediction:
Predicted_Range = Pos_Z - Terrain_State. - Measurement: The Lidar reports a distance.
- Correction: The difference (Innovation) is used to update the
terrainState.- Effect: The EKF "moves the ground" to match the Lidar reading.
3. Optical Flow Fusion
Surprisingly, Optical Flow can also update the Terrain State.
- Logic: If the flow sensor sees the ground moving "too fast" for the current estimated height, it implies the ground is closer than thought.
- Prerequisite: Requires GPS velocity to be trusted.
Height Source Switching
The EKF must decide whether to trust the Barometer or the Rangefinder for its primary Z-axis control. This logic resides in selectHeightForFusion().
- Switching to Rangefinder:
- If
Range < RNG_USE_HGT(percentage) AND speed is low (RNG_USE_SPD). - The EKF resets its Z-Axis origin to match the Rangefinder.
- If
- Switching to Barometer:
- If the drone flies too high (out of range) or too fast.
- It seamlessly blends back to Baro/GPS altitude.
Key Parameters
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
EK3_RNG_USE_HGT |
-1 | (%) Max rangefinder distance (as % of max range) to use for primary altitude. |
EK3_RNG_USE_SPD |
2 | (m/s) Max ground speed to use rangefinder. High speeds over rough terrain cause sensor lag issues. |
EK3_TERR_GRAD |
0.1 | Expected terrain slope. |
Source Code Reference
- Estimator Logic:
AP_NavEKF3_OptFlowFusion.cpp - Source Selection:
AP_NavEKF3_PosVelFusion.cpp