EKF Variance & Innovations
Executive Summary
When the GCS screams "EKF Variance" or "Velocity Variance", it means the autopilot is confused. Specifically, it means the sensor data (GPS/Compass) disagrees with the internal physics model (Inertial Prediction) by a margin that exceeds the allowed safety threshold (Gate).
Theory & Concepts
1. Probability Density Functions (The Bell Curve)
Every sensor measurement is a random variable. The EKF assumes that sensor noise follows a Gaussian Distribution (a Bell Curve).
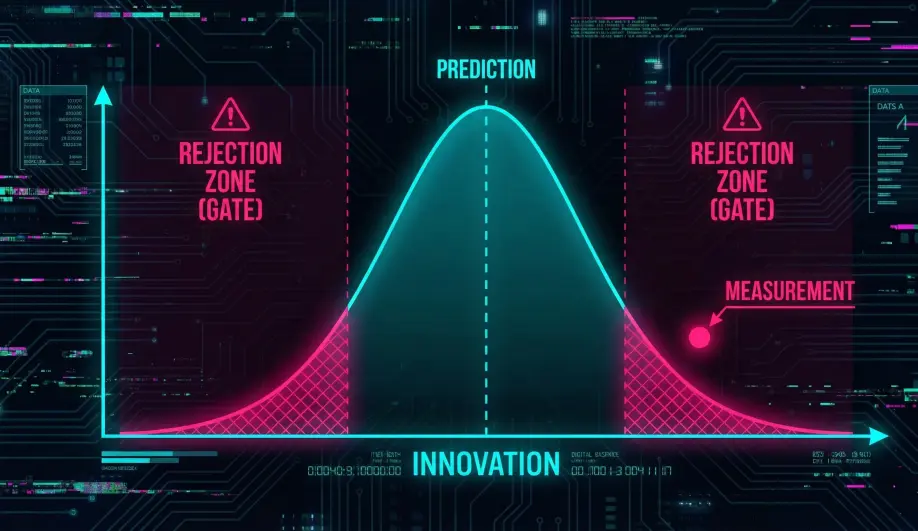
- Innovation: This is the distance from the center of the bell curve.
- Gate (e.g., 5 Sigma): This defines the "cutoff" at the edges of the curve. If a measurement falls outside this gate, there is a 99.99% chance it is a glitch, not real movement.
2. The P Matrix (Covariance)
The EKF maintains a massive 24x24 matrix called the Covariance Matrix (P). It stores the "Confidence" for every state.
- Hovering: Confidence in Position is high.
- GPS Glitch: Confidence drops. The EKF "blooms" its uncertainty, waiting for the GPS to stabilize before trusting it again.
Core Concepts (The Engineer's View)
1. Innovation (The Error)
Innovation is the difference between "What I predicted" and "What I measured".
- Formula:
Innovation = Measurement - Prediction - Example: The EKF predicts the drone is at
X=10m. The GPS reportsX=12m. The Innovation is2m.
2. Variance (The Uncertainty)
Variance describes how much we trust a value.
- Measurement Variance: How noisy is the GPS? (Reported by GPS HDOP).
- State Variance: How sure is the EKF of its own position? (Grows over time if no GPS).
3. The "Test Ratio" (The Trigger)
To decide if a sensor is glitching or if the drone is actually moving, the EKF calculates a Test Ratio.
- Formula:
Ratio = Innovation^2 / (Variance * Gate^2) - Interpretation:
Ratio < 1.0: The measurement is consistent. Fuse it!Ratio > 1.0: The measurement is wildly unlikely. Reject it! (This triggers the "Variance" alert).
The Innovation Gates
You can tune how strict the EKF is using the Gate Parameters.
EK3_VEL_I_GATE: Velocity innovation gate (default 500 = 5 sigma).EK3_POS_I_GATE: Position innovation gate.EK3_HGT_I_GATE: Height innovation gate.
Tuning Trade-off:
- Lower Gate (e.g., 300): The EKF is stricter. It rejects bad GPS data faster (good for safety), but might falsely reject good GPS data during aggressive maneuvers (bad for reliability).
- Higher Gate (e.g., 800): The EKF is permissive. It accepts sloppy GPS data, but if the GPS glitches hard, the drone might "run away" to follow the glitch.
Troubleshooting "Variance" Errors
- Compass Variance: The Compass points North, but the GPS says we are moving East. Innovation spikes.
- Fix: Calibrate Compass or check for interference.
- Velocity Variance: The GPS says we stopped, but the Accelerometer says we are still braking.
- Fix: Check vibration levels (
VIBElog). High vibration makes the Accelerometer "lie," causing the prediction to drift.
- Fix: Check vibration levels (
Source Code Reference
- Calculation Logic:
NavEKF3_core::CalculateVelInnovationsAndVariances()