Magnetometer Management
Executive Summary
The Magnetometer (Compass) is critical for heading, but also the most problematic sensor due to electromagnetic interference. ArduPilot supports multiple compasses, automatic prioritization, and complex orientation handling.
Theory & Concepts
1. Declination: True North vs. Magnetic North
- The Problem: GPS navigation works on True North (Geographic Pole). Compasses point to Magnetic North (which wanders around Canada/Siberia).
- The Correction: ArduPilot uses a lookup table (World Magnetic Model) to find the "Declination" (offset) for your GPS location.
- Why it matters: If you are in New Zealand, the difference is ~20 degrees. If you don't correct for this, your drone will fly sideways (crab) when trying to fly a straight line.
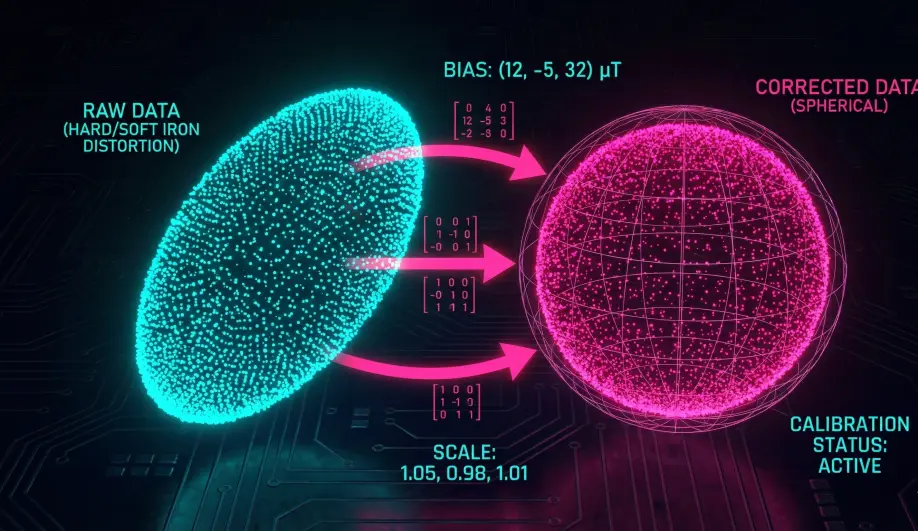
2. Hard Iron vs. Soft Iron Calibration
- Hard Iron (Offsets): A permanent magnet attached to the frame (e.g., a screw, a speaker, or the PDB).
- Effect: It adds a constant bias to the field.
- Calibration: Calculates an X/Y/Z offset to subtract this bias.
- Soft Iron (Scaling): Ferrous metal (steel/iron) that bends the magnetic field lines.
- Effect: It stretches the "Magnetic Sphere" into an ellipsoid.
- Calibration: Calculates a scaling matrix (diagonals) to squish the ellipsoid back into a sphere.
3. Motor Interference (EMF)
- The Physics: Current flowing through a wire creates a magnetic field (Ampere's Law).
- The Effect: When you throttle up, the ESC wires generate a field that twists the compass heading.
- Compassmot: A calibration routine that measures the magnetic shift per Amp of current. ArduPilot subtracts this dynamic offset in real-time.
Architecture (The Engineer's View)
1. Internal vs External
- Internal: Soldered to the Flight Controller.
- Pros: Convenient.
- Cons: Very close to high-current power wires (ESCs). Extremely noisy.
- Handling: Rotated automatically by
AHRS_ORIENTATION. - External: Mounted on the GPS mast.
- Pros: Far from interference.
- Cons: Requires manual orientation.
- Handling: Rotated manually by
COMPASS_ORIENT. It ignoresAHRS_ORIENTATION.
2. Priority Logic
ArduPilot maintains a priority list (COMPASS_PRIO1_ID, etc.).
- Selection: The EKF consumes data from the First Healthy Compass in the priority list.
- Recommendation: Always set your External GPS Compass as
PRIO1_IDand disable the Internals (COMPASS_USE2 = 0,COMPASS_USE3 = 0). This prevents the EKF from falling back to a noisy internal sensor if the external one glitches momentarily.
3. Orientation Logic
The math is specific:
- Read Raw:
(X, Y, Z)from sensor. - Apply Orientation: Apply
COMPASS_ORIENTrotation (e.g., Yaw 180). - Result: The vector must align with the Vehicle's Body Frame (X=Forward, Y=Right, Z=Down).
- Common Error: If you mount a GPS 180 deg rotated, you must set
COMPASS_ORIENTtoYaw180. If you set it toNone, the compass will point backwards, causing "Toilet Bowling".
Key Parameters
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
COMPASS_USE |
1 | Enable/Disable specific compasses. Disable internals! |
COMPASS_ORIENT |
0 | Rotation of the external sensor relative to the frame. |
COMPASS_LEARN |
0 | Legacy "In-Flight Learning". Prefer EKF learning (EK3_MAG_CAL) instead. |
Source Code Reference
- Read Loop:
Compass::read()
Practical Guide: Managing Priorities
The default behavior (using all compasses) is often dangerous because internal compasses are noisy.
Step 1: Identify
- Go to Setup -> Mandatory Hardware -> Compass.
- Look at the IDs.
- External: Usually Compass 1 (on the GPS mast).
- Internal: Usually Compass 2 & 3 (inside the Cube/Pixhawk).
Step 2: Reorder (Priority)
- Ensure the External Compass is at the top of the list (
COMPASS_PRIO1_ID). - If Compass 1 is Internal, use the "Up/Down" buttons to swap priorities.
Step 3: Disable Internals
- Uncheck "Use this compass" for Compass 2 and 3.
- Why? If the external compass fails, falling back to a noisy internal compass (which might be reporting "North is East" due to battery current) is often worse than having no compass at all.
- Exception: If you have dual external GPS units, use both (
PRIO1andPRIO2).