The Parameter Protocol
Executive Summary
Downloading parameters is often the slowest part of connecting a Ground Control Station (GCS). ArduPilot manages over 1000 parameters. Dumping them all at once would choke the link and kill telemetry. The Parameter Protocol uses a cooperative state machine to trickle these parameters down the pipe without interrupting critical flight data.
Theory & Concepts
1. Reliable Transport over Unreliable Links
MAVLink usually runs over UDP (WiFi) or Serial (Radio), both of which are "Lossy." The Parameter Protocol implements its own Reliability Layer. It doesn't use standard TCP-style "sliding windows"; instead, it uses a Request-Response model. The Drone is the "Server" and the GCS is the "Client."
2. State Syncing
The hardest problem in distributed systems is state synchronization. With 1000+ parameters, ArduPilot and the GCS must agree on the "Source of Truth." This is why Bulk Downloads take time: the system is ensuring that every single bit of the flight configuration is identical on both sides of the radio link.
Architecture (The Engineer's View)
The logic resides in GCS_MAVLINK::queued_param_send().
1. The Async Queue (Fast Lane)
When you change a parameter (PARAM_SET) or request a single value (PARAM_REQUEST_READ), the response is queued in a dedicated high-priority buffer (param_replies).
- Processing:
send_parameter_async_replies()checks this buffer first. - Priority: These messages override the bulk download list. This ensures that if you toggle a switch, the GCS updates immediately, even if it's still downloading the full list in the background.
2. The Bulk Iterator (Slow Lane)
When a GCS requests the full list (PARAM_REQUEST_LIST), ArduPilot enters an iterator mode.
- State: It stores a token (
_queued_parameter_token) pointing to the current position in the parameter table. - Step: In each main loop cycle, it sends one parameter if bandwidth allows.
- Throttling: It calculates the available bandwidth and limits parameter traffic to roughly 33% (
1/3). This guarantees that 66% of the link remains free for Attitude, GPS, and Heartbeats.
3. Re-transmission Handling
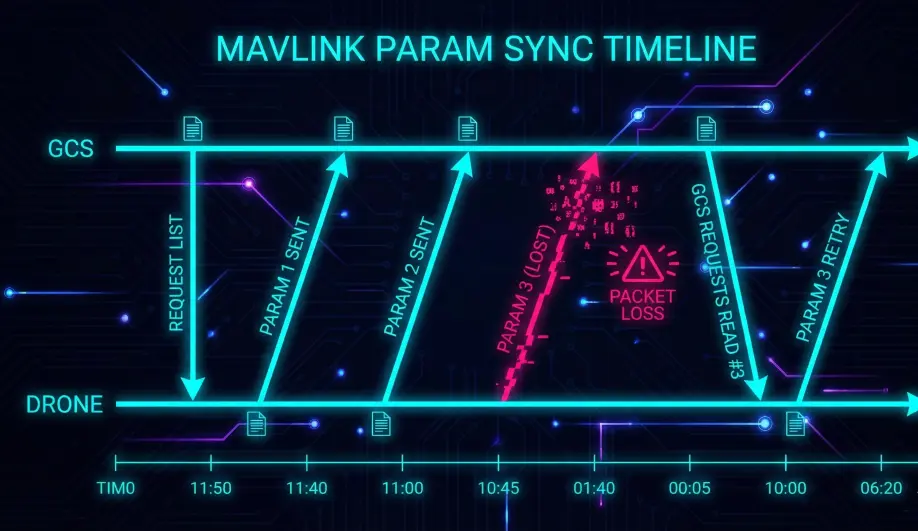
ArduPilot does not track which parameters the GCS has received. It blindly iterates through the list.
- Packet Loss: If a
PARAM_VALUEpacket is dropped, the GCS will notice a gap in the index (e.g., received #5, then #7). - Recovery: The GCS must send
PARAM_REQUEST_READfor the missing index (#6). ArduPilot treats this as a "Fast Lane" async request and replies immediately.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting
"Parameter download gets stuck"
- Cause: High packet loss. The GCS is spending all its time requesting missing packets, saturating the "Fast Lane" and pausing the bulk download.
- Fix: Reduce telemetry rates (
SRx_) to free up bandwidth, or improve radio signal.
"OSD updates are slow while connecting"
- Cause: Even with 33% throttling, the parameter download is a heavy load. The OSD stream might be pushed to lower-priority buckets.
Source Code Reference
- Bulk Sender:
GCS_MAVLINK::queued_param_send() - Async Reply:
GCS_MAVLINK::send_parameter_async_replies()