MAVLink2 Signing & Security
Executive Summary
Standard MAVLink is unencrypted and unauthenticated. Anyone with a radio on the same frequency can inject commands (e.g., "Disarm"). MAVLink2 Signing adds an authentication layer. Every packet includes a cryptographic signature (SHA-256) generated using a secret key. If the signature is missing or invalid, the autopilot rejects the packet.
Theory & Concepts
1. Cryptographic Signatures (HMAC)
MAVLink2 signing uses a concept called HMAC (Hash-based Message Authentication Code). Instead of encrypting the data (hiding it), it signs the data (proving it's real).
- The Key: Both the Drone and GCS have a secret 32-byte key.
- The Signature: We hash the packet with the key. Only someone with the key can produce that specific hash.
- Verification: If the signature doesn't match the packet content, ArduPilot knows the packet was either corrupted by noise or injected by a malicious user.
2. Replay Attacks
A "Replay Attack" is when an attacker records a valid command (like "Disarm") and plays it back later. Even with a cryptographic signature, the packet is valid.
- The Defense: Timestamps. Every signed packet has a unique timestamp. If the timestamp is older than the last one received, ArduPilot rejects it as a replay.
Architecture (The Engineer's View)
The logic is split between the generated MAVLink headers (mavlink_helpers.h) and ArduPilot's key manager (GCS_Signing.cpp).
1. The Signature Block
MAVLink2 adds a 13-byte footer to signed packets:
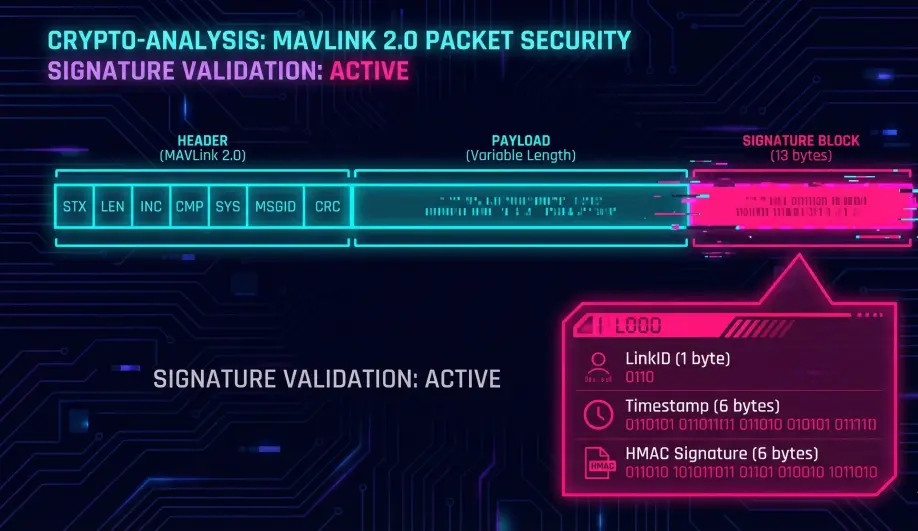
- Link ID (1 byte): Identifies the communication channel (e.g., Radio 1, Wifi).
- Timestamp (6 bytes): 48-bit counter (microseconds since 2015). Critical for Replay Protection.
- Signature (6 bytes): The first 48 bits of the SHA-256 hash.
2. The Mechanics
- Signing (Sender):
Hash = SHA256(SecretKey + PacketContent + Timestamp).- The packet is transmitted with the timestamp and truncated hash.
- Verification (Receiver):
- Receiver calculates
ExpectedHashusing its local copy ofSecretKey. - If
Hash == ExpectedHash, the packet is authentic.
- Receiver calculates
- Replay Protection:
- The receiver tracks the Last Timestamp seen for each Link ID.
- If a new packet arrives with
Timestamp <= LastTimestamp, it is rejected as a Replay Attack (someone recorded an old "Disarm" command and is playing it back).
3. Key Management
The 32-byte Secret Key is the root of trust.
- Storage: Keys are stored in the Flight Controller's persistent storage (FRAM/Flash).
- Setup: The key is usually generated by the Ground Control Station (GCS) and sent to the drone via the
SETUP_SIGNINGmessage.- Constraint: This message is only accepted when the vehicle is Disarmed.
- Code Path:
GCS_MAVLINK::handle_setup_signing().
Common Issues & Troubleshooting
"Bad Signature" / "Link Rejected"
- Cause: Key mismatch between GCS and Drone.
- Fix: Re-run the "Setup Signing" wizard in Mission Planner/QGC to sync a new key.
"Replay Error" after Reboot
- Cause: The GCS clock drifted or reset.
- Fix: The GCS usually handles this by negotiating a new timestamp offset, but sometimes a full restart of both sides is required.
Source Code Reference
- Key Logic:
GCS_MAVLINK::load_signing_key() - Message Handler:
GCS_MAVLINK::handle_setup_signing()
Practical Guide: Enabling Signing
Security is useless if it's too hard to use. Here is the happy path.
Step 1: Generate the Key (Mission Planner)
- Connect to the drone via USB (for reliability).
- Press Ctrl+F (Temp Screen).
- Click "Mavlink Signing".
- Click "Setup Signing".
- Mission Planner will generate a random 32-byte key and upload it to the drone.
- Important: It will also save this key to your PC's
MissionPlanner.xml.
Step 2: Sharing the Key
If you want to use QGroundControl on your tablet, it needs the key too.
- In the Mavlink Signing screen, click "Show Key".
- Copy the 64-character hex string.
- In QGroundControl: Application Settings -> MAVLink -> Signing Key.
- Paste the key.
Step 3: Verification
- Connect via Telemetry Radio.
- Look at the console. You should see
GCS: Signing Activeor similar. - If you try to connect with a GCS that doesn't have the key, the drone will simply ignore it. The GCS will time out waiting for parameters.