DataFlash Structure
Executive Summary
ArduPilot logs are self-describing binary files. They do not require a separate schema file to decode. The first few kilobytes of every .bin log contain FMT (Format) messages that define the structure, labels, units, and multipliers for every other message type in the file.
This efficiency allows ArduPilot to log high-rate data (400Hz+) with minimal CPU overhead compared to text-based formats like CSV or JSON.
Theory & Concepts
1. The Self-Describing Header
Every log starts with a series of FMT messages.
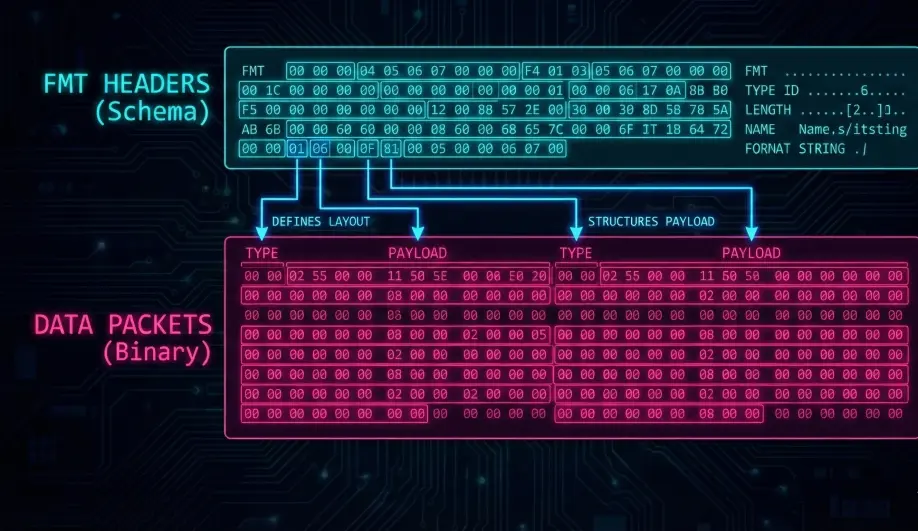
- Format:
Type, Length, Name, FormatString, Labels - Example:
FMT, 128, 89, FMT, BBnNZ, Type,Length,Name,Format,Columns- This message defines the
FMTmessage itself!
- This message defines the
- Format Strings: Characters like
b(int8),f(float),Q(uint64_t) define the C-type of the data.
2. Units & Multipliers
The FMTU message links a Format ID to specific SI units.
UNIT: Defines the base unit (e.g.,sfor seconds,mfor meters).MULT: Defines the scaler (e.g.,F= $10^{-6}$ for microseconds).- Benefit: Analysis tools (Mission Planner, PlotJuggler) can automatically label axes correctly.
Codebase Investigation
1. The Log Structure Definitions: LogStructure.h
Located in libraries/AP_Logger/LogStructure.h.
- This file defines the C-structs that match the on-disk format.
- Packed:
struct PACKED log_ATTensures no padding bytes are inserted by the compiler. - Macros:
LOG_PACKET_HEADERadds the 3-byte sync header (HEAD_BYTE1,HEAD_BYTE2,MSG_ID).
2. Writing Data: AP_Logger::WriteBlock()
Located in libraries/AP_Logger/AP_Logger.cpp.
- Data is written to a ring buffer (
_writebuf). - A background thread (
io_thread) or the main loop (if no thread) flushes this buffer to the backend (SD Card, DataFlash chip, or MAVLink).
Source Code Reference
- Structure Definitions:
libraries/AP_Logger/LogStructure.h - Logger Core:
libraries/AP_Logger/AP_Logger.cpp
Practical Guide: Parsing Logs
If you are writing a custom log parser (e.g., in Python):
- Read Header: Parse all
FMTmessages first. Store them in a map{msg_id: format_obj}. - Read Body: Read byte-by-byte looking for
HEAD_BYTE1(0xA3) andHEAD_BYTE2(0x95). - Decode: Read the
MSG_IDbyte, look it up in your map, readLengthbytes, and unpack using theFormatString.