Power Forensics
Executive Summary
Power failure is the most common cause of non-pilot-error crashes. Analyzing power logs allows you to distinguish between Battery Exhaustion (ran out of capacity), Voltage Sag (over-current/old battery), and Brownouts (flight controller power failure).
Theory & Concepts
1. Voltage Sag vs. Capacity
- Capacity (mAh): The "Fuel" in the tank. Consumed over time.
- Sag (Volts): Instantaneous voltage drop due to load ($V_{drop} = I \times R_{internal}$).
- Danger: High current causes deep sag. If voltage drops below the ESC cutoff (e.g., 3.0V/cell), the ESCs will reboot mid-air even if 50% capacity remains.
2. Brownouts
A brownout occurs when the 5V rail powering the Flight Controller drops below ~4.5V.
- Effect: The MCU resets. Log ends abruptly.
- Cause: Overloaded BEC (too many servos/LEDs) or short circuit.
Codebase Investigation
1. Battery Monitor: AP_BattMonitor::read()
Located in libraries/AP_BattMonitor/AP_BattMonitor.cpp.
- It reads raw ADC values for Voltage and Current.
- Integration:
_consumed_mah += (current_amps * dt) / 3600.0f; - Logging: Writes
BAT(Basic info) andBCL(Cell levels if available).
2. System Power: log_POWR
Vcc: The voltage of the 5V rail powering the board.VServo: The voltage of the Servo rail.
Source Code Reference
- Monitor Core:
libraries/AP_BattMonitor/AP_BattMonitor.cpp
Practical Guide: Forensics
1. The "V" Shape
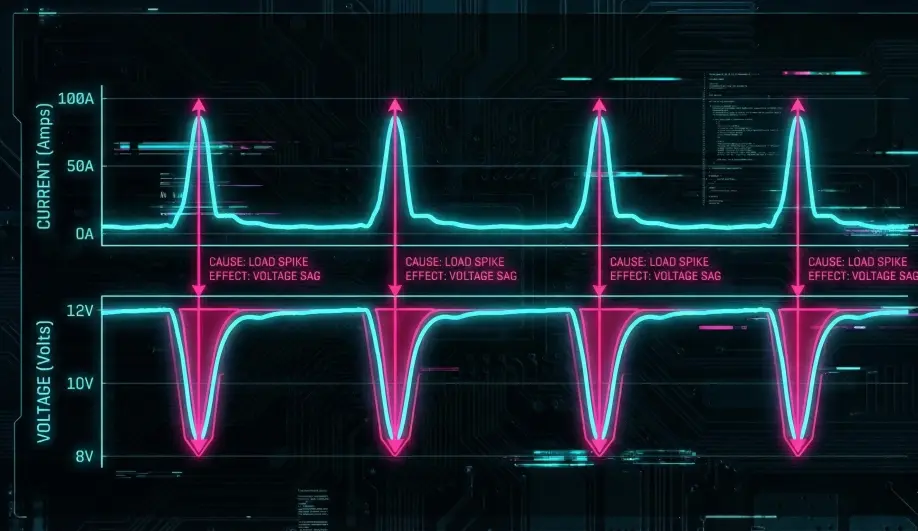
- Look at
BAT.VoltvsBAT.Curr. - If Voltage dips sharply exactly when Current spikes (Throttle Punch), your battery has high internal resistance (old/weak/cold).
- Fix: Use higher C-rated batteries or warm them up.
2. The abrupt End
- If the log ends mid-flight, check
POWR.Vccin the last few seconds. - If
Vccdrifts below 4.8V or has noise, your power module is failing.
3. Total Consumption
- Compare
BAT.CurrTot(mAh used) against your battery's rated capacity. - Rule of Thumb: You should land before using 80% of rated capacity.