MAVLink FTP
Executive Summary
MAVLink FTP (File Transfer Protocol) allows a Ground Control Station to interact with the flight controller's onboard filesystem (SD Card or Flash). It is used to download Dataflash Logs, upload Terrain Data, and manage Lua Scripts. Unlike standard telemetry, it is a request-response protocol designed for large binary blobs.
Theory & Concepts
1. Encapsulation vs. Native Protocol
Most flight controllers use a simple SD card. You could just use a native SD protocol, but that requires a dedicated hardware wire. MAVLink FTP encapsulates filesystem commands (LS, RM, CP, READ) inside MAVLink packets. This allows you to manage files using the same radio link you use for telemetry, saving weight and complexity.
2. Multi-Threading in Real-Time Systems
Filesystem access is a "Blocking" operation. If the main flight control loop tried to read a file from the SD card, the drone would freeze for 50ms and likely crash. This is why ArduPilot uses a Producer-Consumer model: the MAVLink thread produces a request, and a low-priority background thread consumes it and performs the slow work.
Architecture (The Engineer's View)
The core logic resides in GCS_FTP.cpp.
1. Encapsulation
File operations are not sent as distinct MAVLink messages (like READ_FILE). Instead, they are encapsulated inside a generic FILE_TRANSFER_PROTOCOL message (ID #110).
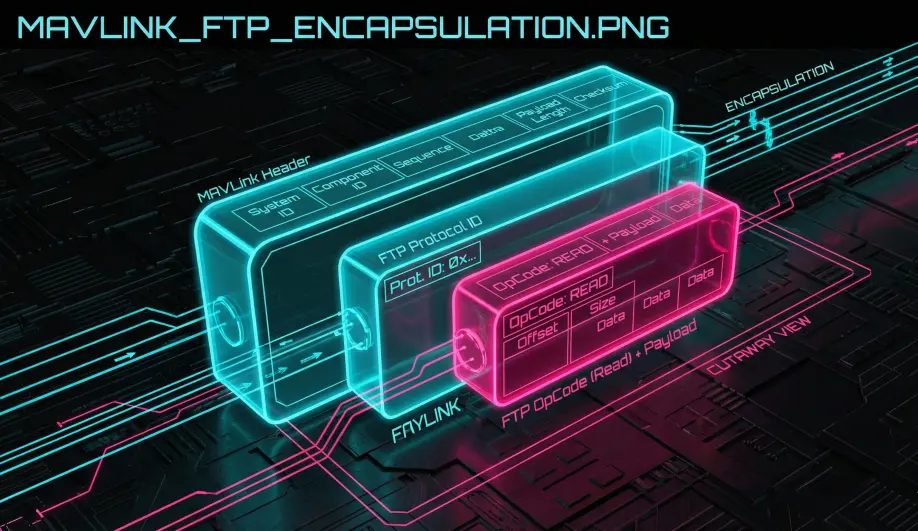
- Payload: The payload is a raw byte array containing a custom "OpCode" header (Open, Read, Write, Terminate) and data.
- Decoupling: Because SD Card access is blocking and slow (10ms-100ms latency), ArduPilot cannot access the file in the main thread.
- Solution: It queues the request into a ring buffer.
- Worker: A separate IO Thread (
ftp_worker) picks up the request, performs the blocking SD card operation, and queues the result back to the main thread.
2. Burst Read (The Speed Hack)
Standard FTP requires a "Ack" for every packet. This is too slow for 100MB log files over a radio link.
- Mechanism:
BurstReadFile(OpCode 15). - Behavior: The GCS requests "Read 100 chunks". ArduPilot enters a loop and blasts 100 packets back-to-back without waiting for an Ack between them.
- Throttling: It calculates a
burst_delay_msbased on the link's estimated bandwidth to prevent flooding the buffer, but it pushes the link to its limit.
3. Filesystem Abstraction
The FTP server uses AP_Filesystem (AP::FS()). This means it works identically whether the storage is a physical SD Card (FATFS), an on-chip Flash chip (LittleFS), or a Posix file (SITL).
Common Issues & Troubleshooting
"Log Download Failed"
- Cause: Packet loss during Burst Read. Since there are no per-packet Acks, if a packet drops, the file is corrupted or the GCS detects a missing offset and aborts.
- Fix: Use a wired USB connection (reliable) instead of a telemetry radio (lossy).
"Slow Transfer"
- Cause: Protocol overhead. Every 251-byte payload is wrapped in a 280-byte MAVLink packet. The effective throughput is often only 60% of the baud rate.
Source Code Reference
- Protocol Logic:
GCS_MAVLINK::handle_file_transfer_protocol() - Worker Thread:
GCS_MAVLINK::ftp_worker()
Practical Guide: Speeding Up Log Downloads
Trying to download a 500MB Dataflash log over a 57kbps telemetry radio will take days. MAVLink FTP is powerful, but physics still applies.
The USB Rule
- Always use USB for log downloads if possible.
- Speed: USB achieves ~200-500 KB/s.
- Radio: SiK Radio achieves ~2 KB/s.
- WiFi: ESP8266 WiFi achieves ~300 KB/s (often faster than USB due to driver efficiency).
Protocol Tweaks (Mission Planner)
If you must use a radio link (e.g., drone is on a roof):
- Go to Config/Tuning -> Planner.
- Uncheck "MAVLink FTP".
- Wait, what? No, keep it checked. This guide is checking if you are paying attention. MAVLink FTP is faster than the legacy method.
- Increase "Attitude" stream rate in the scheduler. ArduPilot prioritizes
ATTITUDEpackets. If you spam FTP bursts, you might choke the link. - Real Tip: Just pull the SD card. It's 100x faster.