System Identification (SysID)
Executive Summary
System Identification (SysID) is an engineering method to build a mathematical model of a physical system by stimulating it with known inputs and measuring the output.
ArduPilot's System ID Mode injects a "Chirp" signal (sweeping frequency sine wave) into the control loops. By analyzing the vehicle's response (Gyro/Accel) compared to the input (Chirp), we can generate Bode Plots to determine the system's bandwidth, phase margin, and optimal PID gains.
Theory & Concepts
1. The Chirp Signal
The "Chirp" is a sinusoidal signal that sweeps from a low frequency to a high frequency over a set duration.
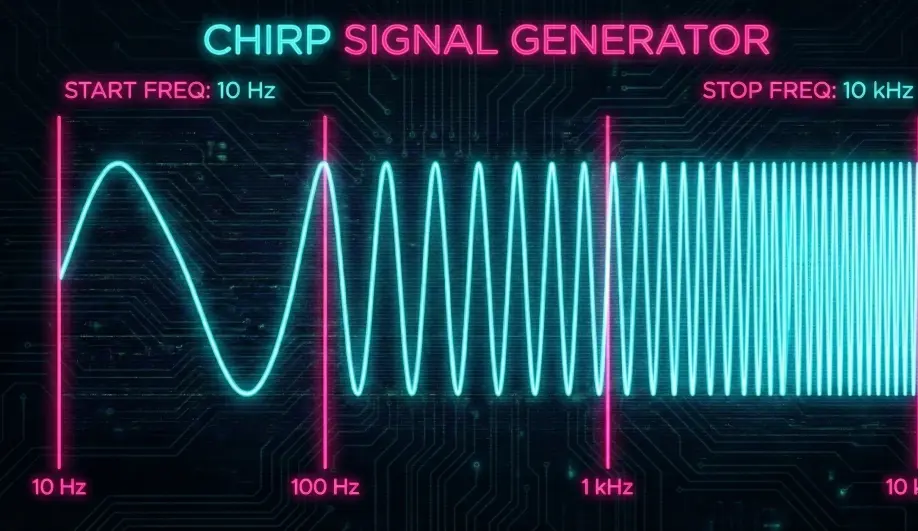
- Start Frequency (f_start): Low frequency to test steady-state response.
- Stop Frequency (f_stop): High frequency (typically 20-40Hz) to test high-speed dynamics and noise rejection.
- Amplitude: The magnitude of the disturbance. It must be large enough to overcome friction/stiction but small enough to prevent the drone from flipping over.
2. Frequency Response Analysis (Bode Plot)
The data from the Chirp is used to generate a Bode Plot, which shows the system's gain and phase lag across the frequency spectrum.
- Gain Margin: How much gain can be added before the system becomes unstable.
- Phase Margin: How much delay (lag) the system can tolerate.
- Bandwidth: The frequency where the system can no longer track the input.
Codebase Investigation
1. The Mode Logic: ModeSystemId::run()
Located in ArduCopter/mode_systemid.cpp.
- It generates the waveform:
waveform_sample = chirp_input.update(waveform_time - SYSTEM_ID_DELAY, waveform_magnitude); - It adds this sample to the target based on SID_AXIS. For example, if
SID_AXIS = 7(Rate Roll):attitude_control->rate_bf_roll_sysid(radians(waveform_sample));
2. Logging
Crucially, SysID logs high-rate data specifically for analysis tools.
SIDDLog Message: Contains Time, Input Value, Current Frequency, and Gyro/Accel response.PIDLogs: The standard PID logs are also critical for verifying tracking.
Source Code Reference
- Mode Implementation:
ArduCopter/mode_systemid.cpp - Chirp Generator:
libraries/AP_Math/control.cpp(SeeChirpclass).
Practical Guide: Running a SysID Flight
1. Safety First
- Space: You need a large, open area. The drone will drift during the test.
- AltHold: SysID usually runs in a mode similar to Althold. You control throttle; the computer controls attitude (with the chirp overlaid).
2. Configuration
SID_AXIS: Start with 0 (None) to get to the field. Set to 1 (Input Roll) or 2 (Input Pitch) for initial tuning.- SID_MAGNITUDE: Start small. 5 degrees for angle, 50 deg/s for rate.
- SID_F_START / SID_F_STOP: 0.5Hz to 20Hz is standard for large quads.
3. The Procedure
- Take off in Loiter/AltHold.
- Switch to System ID Mode.
- Wait. The drone will pause (Fade In), then start oscillating.
- Do not touch the sticks unless it drifts too far. Correcting the drift ruins the data (adds external inputs).
- Wait for the chirp to finish (Fade Out).
- Land and analyze the logs.