System Identification Mode (Copter)
Executive Summary
System Identification (SysID) is an advanced engineering mode designed to mathematically model the vehicle's physical response characteristics. It automatically injects a "Chirp" signal (frequency sweep) into a specific control axis while recording high-speed data logs. This data is used offline to generate Bode plots, identifying the vehicle's bandwidth, delay, and resonance frequencies for precise tuning.
Theory & Concepts
1. Frequency Domain Analysis
Most flight modes operate in the Time Domain (How fast can I move now?). System ID operates in the Frequency Domain (How well can I move at 10 Hz?).
- The Concept: Every drone has a "Resonant Frequency" where the frame or arms vibrate.
- The Test: By sweeping through frequencies, the EKF can find these resonant peaks and automatically configure Notch Filters to ignore them.
2. Bode Plots and Bandwidth
A Bode plot shows the "Gain" and "Phase" of a system.
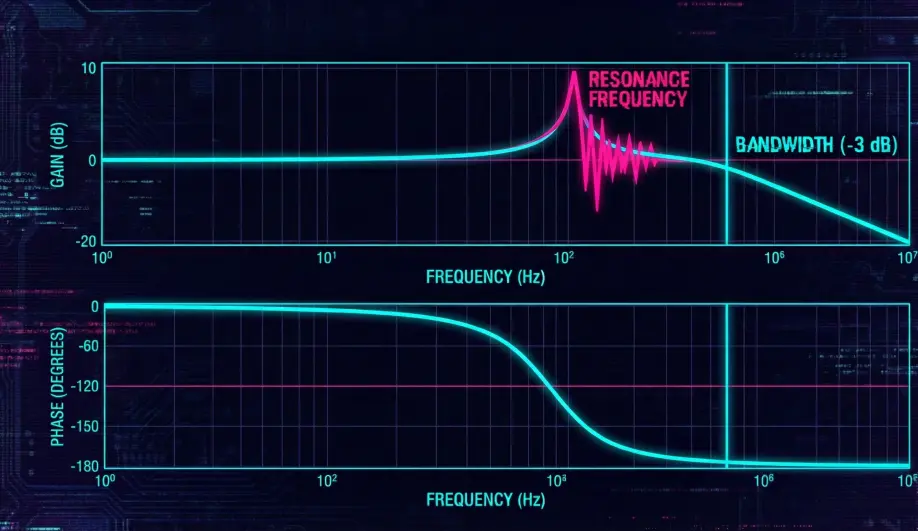
- Gain: If I command 10 degrees, do I actually get 10 degrees?
- Phase: If I command a move, how many milliseconds later does it happen?
- Control Bandwidth: This test reveals the "Speed limit" of your drone's brain. If the bandwidth is 10Hz, the drone cannot react to anything faster than 10 times per second.
Hardware Dependency Matrix
This mode is for data gathering, not navigation.
| Sensor | Requirement | Code Implementation Notes |
|---|---|---|
| SD Card | CRITICAL | Requires high-speed logging. If logging fails, the test is useless. |
| Gyroscope | CRITICAL | The primary sensor being measured against the input chirp. |
| GPS | CONTEXTUAL | Required if identifying Position Controller loops (SID_AXIS > 13). Not required for Rate loops. |
Control Architecture (Engineer's View)
The mode operates as a signal injector overlaid on top of a standard flight mode.
- Signal Generation (
Chirp):- It generates a waveform that sweeps from
SID_F_START_HZtoSID_F_STOP_HZoverSID_T_RECseconds. - The amplitude is defined by
SID_MAGNITUDE.
- It generates a waveform that sweeps from
- Injection Point:
- The chirp is added on top of the pilot's input.
- Example: If
SID_AXIS= 1 (Roll Angle), the controller commandsTarget_Roll = Pilot_Roll + Chirp_Signal. - Benefit: The pilot can still fly the drone to keep it level or away from walls while the jittery chirp test runs.
- Data Logging:
- It writes
SIDS(Setup) andSIDD(Data) messages to the dataflash log at full loop rate (400Hz+).
- It writes
Safety Logic
- Mode Switch Abort: Switching flight modes instantly stops the test.
- Angle Limits: If the vehicle leans past
ANGLE_MAX(due to a violent chirp response), the test aborts. - Landing Detector: If the vehicle lands, the test aborts.
- Entry Checks:
Key Parameters
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
SID_AXIS |
0 | 0=Disabled. 1=Roll Angle, 2=Pitch Angle, 3=Yaw Angle... (See wiki for full list). |
SID_MAGNITUDE |
0 | Amplitude of the injection. Start small! (e.g., 5-10 deg for Angle). |
SID_F_START_HZ |
0.5 | Start frequency of the sweep. |
SID_F_STOP_HZ |
30 | Stop frequency. |
SID_T_REC |
50 | Duration of the sweep (seconds). |
Source Code Reference
- Mode Logic:
ardupilot/ArduCopter/mode_systemid.cpp - Chirp Generator:
Chirp::update()
Practical Guide: The Frequency Sweep
Stop guessing your notch filters. Measure them.
Step 1: Configuration
- Axis: Set
SID_AXIS = 1(Roll Rate). This is the safest to test. - Magnitude: Set
SID_MAGNITUDE = 5(5 deg/s). This is gentle. - Frequency: Start 0.5 Hz, Stop 40 Hz. Duration 60s.
Step 2: The Flight
- Take off in AltHold.
- Hover at a safe height (5m).
- Switch to SystemID mode.
- Hands Off: Try not to touch the Roll stick. The drone will start to "shiver" (low frequency) and then buzz (high frequency).
- Wait: Wait for the test to finish (60s) or until the drone stops buzzing.
- Land and Disarm.
Step 3: Analysis
- Upload the log to the ArduPilot WebTools SysID Plotter.
- Look at the Frequency Response.
- The Peak: If you see a massive spike at 150Hz, that is your frame resonance. Set
INS_HNTCH_FREQ = 150to kill it.