AP_Periph: Building Custom Nodes
Executive Summary
AP_Periph is a stripped-down version of ArduPilot designed to run on peripheral microcontrollers (like STM32F3 or F4) instead of a Flight Controller. It allows you to turn almost any sensor (GPS, Compass, Airspeed, Rangefinder) into a DroneCAN Node.
Theory & Concepts
1. The Distributed Autopilot
Traditional drones are a "Star Topology" (Everything plugs into the center).
AP_Periph enables a "Bus Topology".
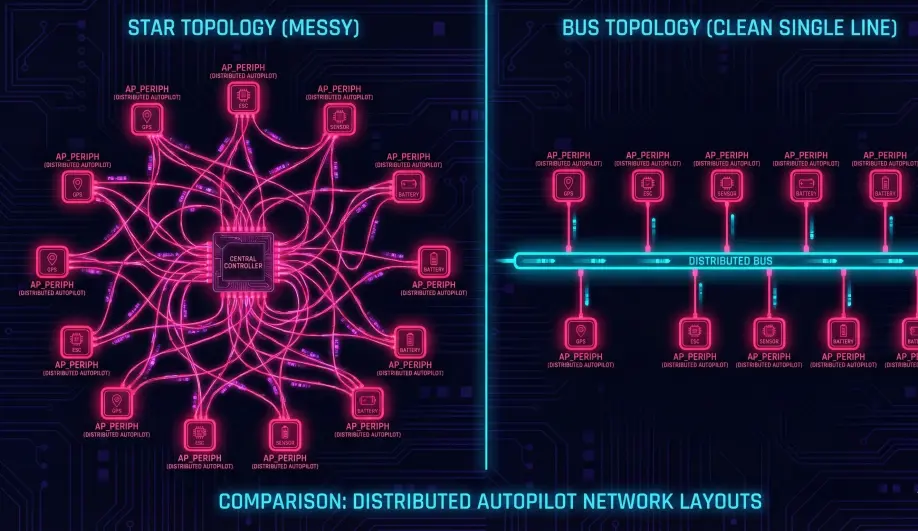
- The GPS Node: Contains a GPS module, a Compass, an RGB LED, and a Buzzer. It runs
AP_Periph. It connects to the Flight Controller with 4 wires (VCC, GND, CAN_H, CAN_L). - The Benefit: Noise isolation. The sensitive compass is far away from the high-current ESCs. The wiring harness is simple.
2. Driver Reuse
AP_Periph does not use "Special" drivers. It links against the standard ArduPilot libraries.
- Implication: If a sensor works in ArduCopter, it works in AP_Periph.
- Maintenance: You don't need to write custom CAN code for a new sensor. You just enable the existing driver in the
hwdef.datand compile.
Architecture (The Engineer's View)
1. The Main Loop (AP_Periph_FW::update)
Unlike ArduCopter (400Hz), AP_Periph runs a simpler loop.
- Sensor Read: It polls all enabled libraries (
AP_GPS,AP_Compass). - CAN Transmit: It packages the sensor data into DroneCAN packets (e.g.,
uavcan.equipment.[gnss](/field-manual/sensor-architecture/gps-integration.html).Fix). - CAN Receive: It listens for configuration parameters from the GCS.
2. The Bootloader
AP_Periph devices use a special bootloader that supports CAN Firmware Updates.
- Mechanism: The Flight Controller acts as a "Bridge." You can flash the GPS firmware through the Flight Controller USB port using the DroneCAN GUI Tool.
Key Parameters
These are set on the Peripheral itself (using the GUI Tool), not the Flight Controller.
CAN_NODE_ID: 0 (Automatic DNA) is standard.GPS_TYPE: Selection of the sensor driver.
Source Code Reference
- Main Loop:
AP_Periph_FW::update() - CAN Handler:
AP_Periph_FW::can_update()