Follow Mode (Copter)
Executive Summary
Follow Mode allows the copter to autonomously track and follow another MAVLink-enabled vehicle (Lead Vehicle) or a Ground Control Station (GCS). It maintains a specific relative offset (distance, altitude, angle) and matches the lead vehicle's velocity vector.
Theory & Concepts
1. Relative Reference Frames
In robotics, there are two ways to describe position:
- Earth-Fixed (Inertial): Latitude and Longitude. (e.g., "Go to North 10m").
- Body-Fixed (Local): Relative to the drone. (e.g., "Move 10m to my right").
- The Follow Problem: To follow a moving person, the drone must constantly calculate its position in the Target's Body Frame. If the person turns, the drone must rotate around them to maintain the same "Over the shoulder" angle.
2. Time Synchronization (Latency)
Following is a "Chase" problem.
- The Latency: The leader sends its position over radio. By the time the follower receives it, the leader has already moved.
- The Correction: ArduPilot uses Velocity Extrapolation. It takes the leader's Speed and Heading to predict where they will be 200ms in the future, aiming the drone at the future point rather than the stale past point.
Hardware Dependency Matrix
Both the follower (your drone) and the leader must have precise positioning.
| Sensor | Requirement | Code Implementation Notes |
|---|---|---|
| GPS | CRITICAL | Required on BOTH vehicles. The follower needs its own position to calculate the vector to the leader's reported position. |
| Compass | CRITICAL | Required for heading control and offset calculations. |
| Telemetry | CRITICAL | A MAVLink data link (SiK Radio, Wifi, ELRS bi-directional) is required to receive GLOBAL_POSITION_INT messages from the lead vehicle. |
Control Architecture (Engineer's View)
Follow Mode is effectively a dynamic wrapper around Guided Mode.
- Target Estimation (
AP_Follow):- The vehicle listens for MAVLink messages (ID #33
GLOBAL_POSITION_INTor #144FOLLOW_TARGET). - It filters this data to estimate the lead vehicle's Position and Velocity.
- It applies the user-defined Offsets (
FOLL_OFS_X/Y/Z) to calculate a "Virtual Target Point" where the follower should be.
- The vehicle listens for MAVLink messages (ID #33
- Velocity Controller:
- Instead of just flying to the waypoint (which would cause lag), the controller uses Feed-Forward Velocity.
Target_Velocity = Lead_Velocity + Position_Error_Correction.- This allows the drone to match speed perfectly without lagging behind.
- The computed velocity is passed to the
ModeGuidedvelocity controller logic.
Offsets & Reference Frames
Understanding the Reference Frame (FOLL_OFS_TYPE) is critical for predictable behavior.
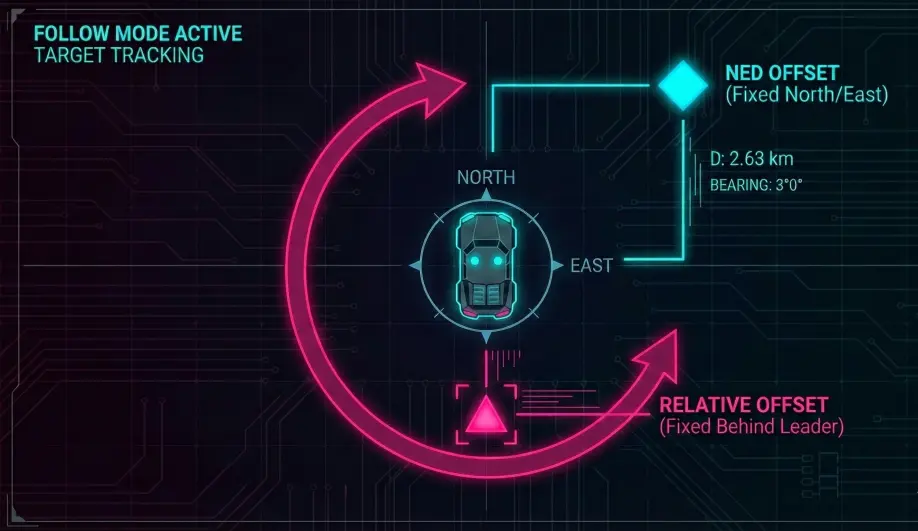
- NED Frame (Type 0): Offsets are Earth-fixed (North/East).
- Example: If Offset X = 10, the drone stays 10 meters North of the leader, regardless of which way the leader is flying.
- Relative Frame (Type 1): Offsets are Body-fixed to the Leader.
- Example: If Offset X = -10, the drone stays 10 meters behind the leader. If the leader turns 90 degrees, the drone orbits to stay behind it.
Failsafe Logic
- Target Loss: If the MAVLink stream is interrupted for more than 3 seconds (
AP_FOLLOW_TIMEOUT_MS), the vehicle stops tracking.- Behavior: It sets the desired velocity to zero and effectively enters a PosHold state until the signal returns.
- GPS Loss: Standard EKF failsafes apply (Land or AltHold).
Key Parameters
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
FOLL_SYSID |
0 | The MAVLink System ID of the lead vehicle to track. 0 = track the first vehicle seen. |
FOLL_OFS_X |
0 | (meters) Distance offset (Forward/North). |
FOLL_OFS_Y |
0 | (meters) Distance offset (Right/East). |
FOLL_OFS_Z |
0 | (meters) Altitude offset (Down). Negative values = higher than leader. |
FOLL_OFS_TYPE |
1 | 0=NED (North/East), 1=Relative (Forward/Right). |
FOLL_POS_P |
0.1 | Gain for position error correction. Higher values close the gap faster but may overshoot. |
Source Code Reference
- Mode Logic:
ardupilot/ArduCopter/mode_follow.cpp - Message Handler:
AP_Follow::handle_msg()