Guided Mode (Copter)
Executive Summary
Guided Mode is the primary interface for "Offboard Control." While Auto mode runs a pre-uploaded mission, Guided mode listens for real-time commands from a Ground Control Station (GCS) or Companion Computer. It can fly to a specific point, hold a velocity vector, or accept direct attitude targets, making it the mode of choice for swarm operations and dynamic path planning.
Theory & Concepts
1. Offboard Control Hierarchy
In advanced drone systems, "Guided Mode" is the portal between the Low-Level Autopilot (ArduPilot) and the High-Level Brain (ROS, Python script, or GCS).
- The Interface: The High-Level brain makes decisions (e.g., "There is a person, fly to them"). It sends a high-level command to ArduPilot.
- The Execution: ArduPilot handles the difficult part: the PIDs, the Motor Mixer, and the EKF stabilization required to reach that point.
2. Slew Rates
Real physical objects cannot change speed instantly.
- The Concept: If a companion computer asks for 20m/s instantly, the drone would tilt violently and crash.
- The Solution:
GUIDED_SLEW_SPD. ArduPilot applies a low-pass filter to the incoming external commands, ensuring the drone accelerates at a safe, physically attainable rate.
Hardware Dependency Matrix
Guided mode requires robust positioning to execute external commands.
| Sensor | Requirement | Code Implementation Notes |
|---|---|---|
| GPS | CRITICAL | Required for all Position and Velocity sub-modes. Only the Angle sub-mode might run without it (if GUIDED_NOGPS is used, but standard Guided requires it). |
| Compass | CRITICAL | Required for heading control. |
| Telemetry | CRITICAL | A bi-directional link (MAVLink) is required to send commands. |
Control Architecture (Engineer's View)
Guided Mode is a "Meta-Mode" with its own internal state machine, switching logic based on the type of MAVLink message received.
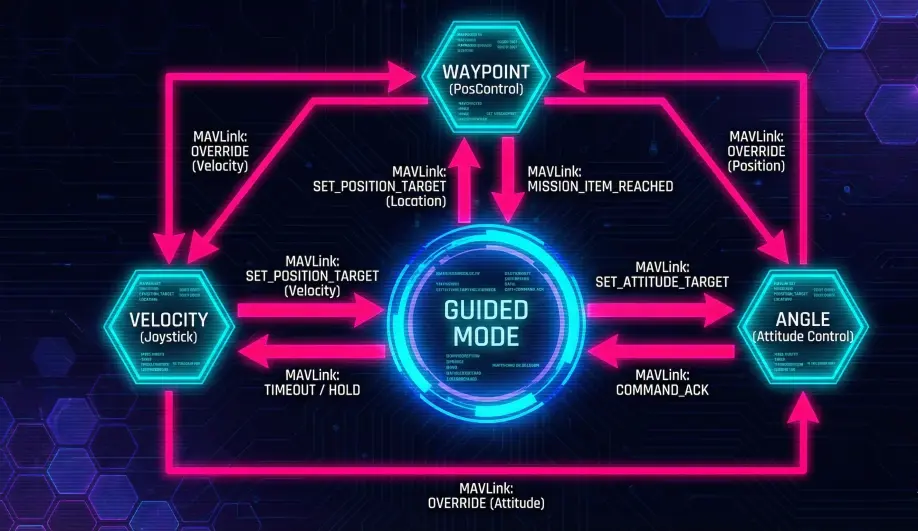
- Waypoint (WP) State:
- Trigger:
SET_POSITION_TARGET_GLOBAL_INT(with Position only) or "Fly To" clicks on a map. - Behavior: Uses
AC_WPNav(same as Auto) to generate a smooth path to the target.
- Trigger:
- Velocity/Accel State:
- Trigger:
SET_POSITION_TARGET_LOCAL_NED(with Velocity bitmask). - Behavior: Passes velocity vectors directly to the Position Controller. Used for "Joystick" control or Companion Computer path following.
- Trigger:
- Angle (Attitude) State:
- Trigger:
SET_ATTITUDE_TARGET. - Behavior: Bypasses the position controller and feeds lean angles directly to the Attitude Controller. Used for aggressive maneuvering or non-GPS fallback.
- Trigger:
Safety & Timeouts
Because Guided mode relies on an external stream of commands, it has a built-in "Deadman Switch."
- Logic: If the vehicle is in a high-frequency control state (Velocity, Accel, or Angle) and stops receiving MAVLink messages for
GUID_TIMEOUTseconds (default 2.4s), it triggers a safety reaction. - Reaction:
- Velocity/Accel: The target velocity is set to zero (stops and holds position).
- Angle: The vehicle attempts to level out.
- Note: The "Waypoint" state does not timeout; once sent, the drone will fly to the destination even if the link is lost.
Key Parameters
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
GUID_TIMEOUT |
2.4 | (seconds) The timeout for streaming commands (Velocity/Attitude). Does not apply to "Go To" waypoints. |
GUID_OPTIONS |
0 | Bitmask. Bit 2: Ignore Pilot Yaw. Bit 6: Use "Thrust" field as direct throttle instead of climb rate. |
WPNAV_SPEED |
500 | Max speed for "Go To" commands. |
Source Code Reference
- Mode Logic:
ardupilot/ArduCopter/mode_guided.cpp - State Dispatcher:
ModeGuided::run() - Command Interface:
ModeGuided::set_destination()
Practical Guide: Companion Computer Safety
When writing code (Python/ROS) to drive Guided Mode, you are the pilot. You must implement your own safety checks.
1. The Heartbeat (Deadman Switch)
If your script crashes, the drone will keep executing the last velocity command forever (until GUID_TIMEOUT kicks in).
- Configure: Set
GUID_TIMEOUT = 0.5(500ms). - Logic: Your script MUST send a command at least every 200ms (5Hz).
- Result: If your script freezes, the drone stops in 0.5 seconds. The default 2.4s is too long for indoor flight.
2. Velocity Smoothing
Your vision system might be noisy, sending "jittery" velocity targets.
- Parameter:
GUID_SLEW_SPD(note: verify name in full param list, typically related to WPNAV or POS control filtering). - Alternative: Use
WPNAV_ACCELto limit how fast the velocity controller can ramp up. - Best Practice: Filter your velocity commands before sending them to ArduPilot. A simple low-pass filter in Python makes the drone fly 10x smoother.