Smart RTL Mode (Copter)
Executive Summary
Smart RTL (Return to Launch) is a sophisticated variation of the standard RTL mode. Instead of flying a straight line home at a fixed altitude, it backtracks along the exact path the vehicle traveled. This is invaluable when flying around obstacles (like behind a building or under trees) where a straight-line return would result in a crash.
Theory & Concepts
1. The Breadcrumb Algorithm
Smart RTL is a classic Breadcrumb algorithm.
- The Problem: GPS signals only tell you where you are, not where it's safe to fly.
- The Logic: "If I flew through here successfully 2 minutes ago, it's probably safe to fly through here again now."
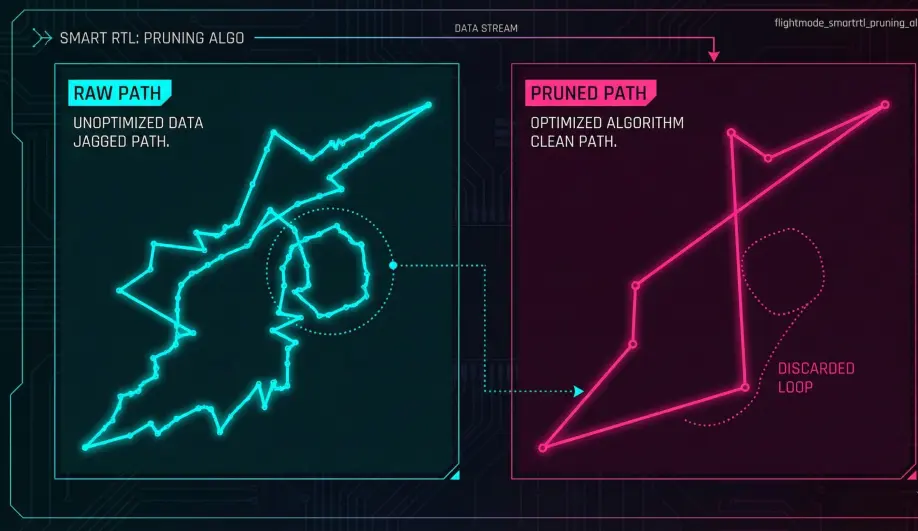
- Path Pruning: To avoid wasting memory on every tiny movement, ArduPilot uses the Douglas-Peucker Algorithm. It analyzes the path and keeps only the "Corner" points, discarding redundant points on a straight line.
2. Safeguard vs. Beeline
Standard RTL is a "Beeline"—it takes the shortest distance. Smart RTL is a "Safeguard"—it takes the proven distance. ArduPilot will choose the proven distance whenever possible to maximize airframe safety.
Hardware Dependency Matrix
Smart RTL is resource-intensive and relies on precise tracking.
| Sensor | Requirement | Code Implementation Notes |
|---|---|---|
| GPS | CRITICAL | Requires a 3D Lock to record the path points. If GPS is lost during flight, path recording stops. |
| Compass | CRITICAL | Required for heading control during the return. |
| Memory | CRITICAL | The flight controller allocates a specific buffer (SRTL_POINTS) to store the path. |
Control Architecture (Engineer's View)
Smart RTL relies on the AP_SmartRTL library to record and optimize the path in real-time.
- Path Recording:
- As you fly, the controller records your position every
SRTL_ACCURACYmeters (default 2m). - It stores these as 3D vectors in a ring buffer.
- As you fly, the controller records your position every
- Path Optimization (Pruning):
- To save memory, a background task constantly "prunes" the path.
- Simplification: It removes points that form a straight line (Ramer-Douglas-Peucker algorithm).
- Loop Closing: If you fly in a circle and cross your own path, it "cuts the loop," discarding the circle segments. This ensures the return path is always the shortest safe route back.
- Execution:
Failsafe Logic
- Buffer Overflow: If the buffer fills up (e.g., a very long, complex flight), the system stops recording new points.
- Warning: Users should monitor the
SRTLmessages. If the buffer is full, Smart RTL might not bring you all the way back to the latest point, but it will still backtrack the recorded path. - Hard Failsafe: If
SRTLcannot initialize (e.g., bad GPS at takeoff), the system automatically falls back to Standard RTL or Land.
- Warning: Users should monitor the
- GPS Loss: If GPS is lost in flight, the path becomes invalid. Smart RTL will fail to engage, forcing a fallback to Land/AltHold.
Key Parameters
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
SRTL_ACCURACY |
2.0 | (m) Min distance between recorded points. |
SRTL_POINTS |
300 | Max number of points to record. 300 points @ 2m spacing = ~600m of unique path (loops don't count). |
RTL_ALT |
1500 | (cm) Minimum return altitude. |
RTL_SPEED |
0 | Return speed (0 = WPNAV_SPEED). |
Source Code Reference
- Mode Logic:
ardupilot/ArduCopter/mode_smart_rtl.cpp - Library Logic:
AP_SmartRTL
Practical Guide: Testing Smart RTL
Before trusting your drone to backtrack autonomously, verify the buffer logic.
1. The "U" Test
- Take off in Loiter.
- Fly 20m forward.
- Fly 20m Right.
- Fly 20m Back (forming a 'U' shape).
- Engage Smart RTL.
- Observation: The drone should fly Forward -> Left -> Backward (retracing the U).
- Failure: If it flies diagonally straight to home, Smart RTL failed (or buffer was empty) and it fell back to Standard RTL.
2. The Loop Cut
- Fly a complete circle (starting and ending at the same spot).
- Fly 10m away.
- Engage Smart RTL.
- Observation: The drone should fly straight back to the circle start point, ignoring the loop. This confirms the pruning algorithm is saving memory.